
At its core, organic vegetable fertilizer is simply plant food that comes from something that was once alive. Think compost, well-rotted animal manure, or meals made from plants like alfalfa or kelp. Instead of dousing your plants with synthetic chemicals, you're feeding the soil's vast ecosystem, which in turn nourishes your vegetables for slow, steady, and healthy growth. It’s a long-term strategy for building vibrant soil, not just a quick chemical fix.
Why Organic Vegetable Fertilizer Is Your Garden's Best Friend

It helps to stop thinking of your garden soil as just "dirt" and start seeing it as a bustling underground city. This city is alive, teeming with billions of earthworms, beneficial bacteria, and fungi all working in harmony. Using an organic vegetable fertilizer is like sending a shipment of wholesome, nutritious food to this entire community. You're building a strong foundation from the ground up.
Synthetic fertilizers, on the other hand, are more like a jolt of caffeine and sugar. They give your plants a sudden, often dramatic, burst of energy but do absolutely nothing to feed that underground city. Over time, these harsh chemicals can actually degrade the soil's structure, kill off the beneficial microbes, and create weak plants that depend on constant chemical inputs to survive. It's a short-term gain that can lead to long-term pain for your garden.
Building Health from the Ground Up
The real magic of organic fertilizers is that they don't just feed the plant; they fundamentally improve the soil itself. This is the key difference. By adding rich organic matter, you’re helping your soil hold onto moisture, creating air pockets for healthy roots to breathe, and fostering a resilient ecosystem that naturally fends off pests and diseases.
This approach pays dividends far beyond a single plant or growing season:
- Long-Term Soil Fertility: Instead of stripping nutrients, you’re actively banking them for the future. You're building a more fertile and productive garden for years to come.
- More Nutritious Vegetables: It just makes sense—healthy, living soil produces healthier plants. Vegetables grown this way are often richer in nutrients.
- Environmental Protection: Organic methods mean no synthetic chemical runoff polluting our local waterways, which protects wildlife and our shared water sources.
Choosing organic is about creating a partnership with your garden. You're not just a planter and a picker; you become a soil steward, building a foundation that supports robust, healthy plants naturally.
A Growing Movement
This shift toward organic thinking isn't just a niche backyard trend; it’s part of a major global movement. As more people catch on to the benefits of sustainable growing, the demand for organic fertilizers is soaring. The global market, valued at USD 9.26 billion in 2025, is on track to nearly double within the next decade.
To see the bigger picture, it's helpful to understand how these practices fit within broader eco-friendly landscaping principles. It's all connected. By choosing an organic vegetable fertilizer, you’re making a smart investment in the future health of your garden, your family, and the environment.
Understanding the N-P-K of Organic Fertilizers

Walking into the fertilizer aisle can feel like you've stumbled into a chemistry class. Every bag is plastered with a set of three numbers, but decoding them is much easier than it looks. Those numbers are the fertilizer's N-P-K ratio, and they're the single most important clue to what that bag can do for your garden.
Think of N-P-K as the "big three" macronutrients for your vegetables. Each one plays a unique and vital role in helping your plants thrive. Getting the balance right is one of the foundational secrets to a truly productive garden.
The Green Growth Engine: Nitrogen (N)
Nitrogen is all about building big, beautiful green leaves. It’s the main ingredient in chlorophyll, which plants use to turn sunlight into food. In short, nitrogen is the fuel for growing stems and leaves.
When a plant gets plenty of nitrogen, it shows. You'll see vibrant, deep green growth. This is especially important for leafy greens that we love to eat, such as:
- Lettuce
- Spinach
- Kale
- Cabbage
A fertilizer with a high first number (like a 4-3-3) is loaded with nitrogen and will give these leafy crops the boost they need. But be careful—giving too much nitrogen to a fruiting plant like a tomato can backfire, resulting in a giant, leafy plant with hardly any flowers or fruit.
The Root and Fruit Builder: Phosphorus (P)
Phosphorus is the plant's master architect. Its main job is to kickstart strong root development, encourage plenty of flowers, and help the plant produce fruit and seeds. Think of it as the energy-transfer specialist, moving power where it's needed most.
A strong root system is the foundation of a healthy plant, anchoring it and pulling in water and nutrients from the soil. Phosphorus is what helps your tomatoes, peppers, and squash produce a flurry of blossoms that eventually become your harvest. Root veggies like carrots and beets also depend on it for healthy development underground.
The Plant Protector: Potassium (K)
Consider potassium the guardian of your garden. It acts like a plant's immune system, overseeing its general health and toughness. This crucial nutrient helps plants manage water, strengthens their cell walls, and gives them the resilience to fend off diseases and stress from heat or cold.
A plant with enough potassium is simply hardier. It can handle a dry spell better and is less likely to fall prey to common fungal diseases. This makes potassium a non-negotiable for the all-around vigor of every vegetable, from sturdy corn stalks to disease-resistant cucumbers. This added resilience is a huge plus for cool-weather crops, a key point when you're planning your garden. You can find out more about which vegetables to plant for the fall season in our detailed guide.
An organic vegetable fertilizer labeled "5-2-4" contains 5% nitrogen for leafy growth, 2% phosphorus for roots and flowers, and 4% potassium for overall plant health. The rest is made up of valuable organic matter and other micronutrients that build healthy soil.
Beyond the Big Three: Micronutrients
While N-P-K are the macronutrients, plants also need a host of micronutrients—just in smaller doses. Think of them as essential vitamins. These include elements like calcium, famous for preventing blossom end rot on tomatoes, and magnesium, a central component of chlorophyll.
This is where organic fertilizers really shine. Unlike synthetic formulas that often just deliver a blast of N-P-K, organic options come from natural sources like kelp meal, alfalfa meal, or rich compost. These materials are naturally packed with a whole spectrum of micronutrients, ensuring your plants get a complete, balanced diet for robust health from the ground up.
What’s Really in Your Organic Vegetable Fertilizer? A Look at the Ingredients
Think of your garden’s soil as a pantry. To grow the best vegetables, you need to stock that pantry with the right ingredients. An organic fertilizer is essentially a curated recipe, with each component chosen to nourish your plants in a specific way. Getting to know these building blocks is the key to moving beyond guesswork and learning to give your garden exactly what it needs to thrive.
Most of these ingredients fall into one of two camps: animal-based sources or plant-based powerhouses. Each type brings a different set of nutrients to the table and releases them at its own pace. This is fantastic news for gardeners, as it allows you to customize your feeding strategy for everything from leafy lettuce to hefty root vegetables, whether you're buying a pre-made mix or blending your own.
Animal-Based Sources
Animal-based amendments are the heavy hitters of the organic fertilizer world. They are often packed with concentrated doses of the key elements plants absolutely crave, delivering powerful and noticeable results.
- Bone Meal: Just what it sounds like—finely ground animal bone. This stuff is an incredible source of phosphorus (P) and calcium. Phosphorus is the magic ingredient for developing strong roots, beautiful flowers, and plenty of fruit. Bone meal is a slow-release amendment, breaking down over months to provide a steady food source. It's a must-have for root veggies like carrots and beets, and fruiting plants like tomatoes and peppers will thank you for it.
- Blood Meal: This is dried and powdered animal blood, and it's one of the most potent sources of natural nitrogen (N) you can find. Nitrogen is what fuels all that lush, green, leafy growth. Unlike bone meal, blood meal works fast, giving plants an almost immediate boost. That makes it perfect for heavy feeders like kale, spinach, and lettuce that need a quick pick-me-up.
- Fish Emulsion and Fish Meal: These are nutrient-rich byproducts from the fishing industry. Fish emulsion is a liquid fertilizer that gives plants a quick but gentle dose of nitrogen and trace minerals, making it fantastic for delicate seedlings and new transplants. Fish meal, its dry and granular cousin, offers a slower, more sustained release of both nitrogen and phosphorus.
The shift towards these natural inputs is changing how we garden and farm on a massive scale. The organic fertilizers market, valued at USD 12.6 million in 2024, is projected to soar to nearly USD 13.28 billion by 2025. These products don’t just feed plants; they improve soil structure, boost microbial life, and even help sequester carbon. You can discover more research on the organic fertilizer market to see just how big this movement has become.
This image gives you a great at-a-glance comparison of the N-P-K values for some common organic materials.
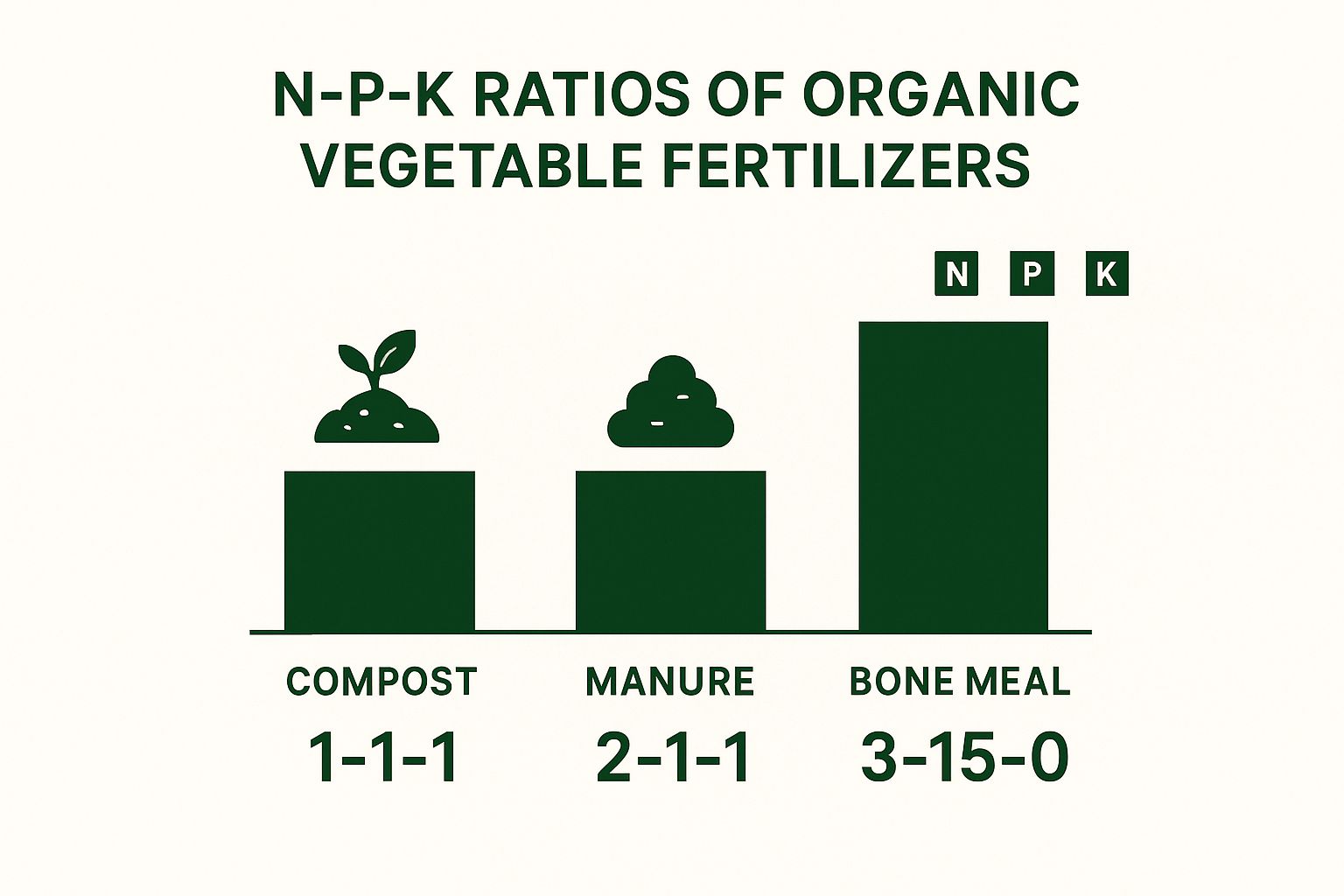
As you can see, something like bone meal delivers a huge phosphorus punch, while compost offers a more balanced, gentle nutrient profile across the board.
Plant-Based Powerhouses
Plant-based fertilizers are incredible for building great soil structure while also delivering a wide range of nutrients. They work by feeding the tiny microbes in your soil, creating a healthier, more fertile environment for the long haul.
- Compost: Gardeners call it "black gold" for a reason. Compost is the ultimate soil conditioner. It’s made from decomposed organic matter and provides a balanced, slow-release mix of all the major nutrients, plus a ton of essential micronutrients. While its N-P-K ratio is usually pretty low (around 1-1-1), its real power is in adding rich organic matter and beneficial microbes back into the soil.
- Alfalfa Meal: Made from fermented alfalfa, this is a real favorite among organic gardeners for its balanced nutrients and growth-boosting compounds. It provides a solid amount of nitrogen and works as a fantastic all-around conditioner to mix into your beds before planting.
- Kelp Meal: Harvested from the sea, dried kelp is a powerhouse of micronutrients and, most importantly, potassium (K). Potassium is vital for a plant's overall vigor, its ability to fight off disease, and how well it manages water. Kelp meal is especially great for long-lasting plants. If you're curious about which crops will stick around for years, you can learn more from our guide on how to choose and grow perennial vegetables.
To help you keep these ingredients straight, here's a quick-reference table.
Common Organic Fertilizer Ingredients and Their Uses
| Ingredient | Primary Nutrients (N-P-K) | Release Speed | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bone Meal | High Phosphorus (e.g., 3-15-0) | Slow | Root vegetables (carrots, beets), flowering/fruiting plants (tomatoes, peppers), bulbs |
| Blood Meal | High Nitrogen (e.g., 12-0-0) | Fast | Leafy greens (lettuce, kale, spinach), corn, heavy-feeding annuals |
| Fish Emulsion | Balanced (e.g., 5-1-1) | Fast | Seedlings, transplants, general-purpose liquid feeding |
| Compost | Low & Balanced (e.g., 1-1-1) | Very Slow | All-purpose soil conditioning, improving soil structure, long-term fertility |
| Alfalfa Meal | Balanced (e.g., 3-1-2) | Medium | General soil preparation, roses, conditioning for all vegetable types |
| Kelp Meal | High Potassium & Micronutrients (e.g., 1-0-2) | Slow to Medium | All vegetables, especially long-lived perennials, improving stress/drought resistance |
This table is a great starting point for mixing and matching ingredients to create the perfect blend for whatever you're growing.
A Gardener's Tip: The best strategy is usually a mix-and-match approach. Try combining slow-release sources like compost and bone meal with a fast-acting one like fish emulsion. This creates a dynamic fertilizer that feeds your plants both for the long haul and for their immediate needs.
Once you understand what each of these core ingredients brings to the garden, you can stop just feeding your plants and start truly building a healthy, thriving ecosystem from the ground up. The result? Healthier soil, stronger plants, and a much more rewarding harvest, season after season.
Choosing Between Commercial and Homemade Fertilizers

When it comes to feeding your vegetable garden, you'll eventually find yourself at a crossroads: should you buy your fertilizer or make it yourself? This isn't just a simple choice. It's really a decision that balances convenience against control and your money against your time.
Honestly, both commercial and homemade fertilizers can help you grow a spectacular harvest. They just take you there on different paths. The "buy or build" dilemma is a classic one for home gardeners, and there's no single right answer. By getting a feel for the pros and cons of each, you can figure out the best strategy for your lifestyle, budget, and gardening goals.
The Case for Commercial Organic Fertilizers
Let's face it: walking into a garden center offers a world of convenience. Commercial organic fertilizers are precisely formulated, tested, and ready to use right out of the bag. This is a fantastic option for gardeners who are short on time, don't have a lot of space, or need to tackle a specific nutrient deficiency with pinpoint accuracy.
But not all bags are created equal. To make a smart choice, you have to look past the big N-P-K numbers on the front. Keep an eye out for the OMRI Listed® seal on the package. This is your guarantee that the product has been independently checked to meet strict organic standards, so you know it's free of synthetic chemicals.
Commercial fertilizers also come in a few different forms, and each has its place in the garden:
- Granular: These are the familiar dry, pellet-like fertilizers you mix into the soil or sprinkle around your plants. They're typically slow-release, providing a steady, gentle stream of nutrients over weeks or months.
- Liquid: Usually sold as a concentrate you mix with water, liquid fertilizers like fish emulsion give your plants a fast-acting nutrient boost. They're perfect for giving new transplants a quick start or for a mid-season "pick-me-up" for heavy feeders like tomatoes.
- Spikes: Think of these as the ultimate "set it and forget it" option. They are compressed, solid spikes of fertilizer that you just push into the soil near a plant's roots, where they'll gradually feed your plants all season long.
The Power of Homemade Fertilizer Blends
For gardeners who love a good DIY project, making your own organic fertilizer gives you total control and can be incredibly budget-friendly. You get to be the chef, tailoring the nutrient recipe to what your garden actually needs. You can use simple, single-ingredient amendments or create custom blends for different types of vegetables.
This approach is about more than just saving money; it’s about getting more connected to the whole gardening process and using resources you might already have around your home.
Creating your own fertilizer blend is the ultimate expression of the organic gardening philosophy: feed the soil, and the soil will feed the plants. You are building a custom diet for your garden's living ecosystem.
Here are a couple of my favorite straightforward "recipes" to get you started.
All-Purpose Vegetable Garden Blend
This is a fantastic, balanced blend to work into your beds before you plant anything. It provides a solid foundation of nutrients that will release slowly throughout the season.
- 4 parts seed meal (like alfalfa or soybean meal) for balanced nitrogen.
- 1 part bone meal or rock phosphate for a strong phosphorus boost for roots and fruits.
- 1 part kelp meal for potassium and a ton of essential trace minerals.
Just mix these ingredients together thoroughly in a bucket. You can then add a few handfuls to each planting hole or just work it into the top few inches of your garden soil.
Fruiting Plant Bloom Booster
Once they start flowering, fruiting plants like tomatoes, peppers, and squash get really hungry for phosphorus and potassium. This mix is designed to give them exactly that.
- Start with your base: Use a gallon of finished compost as your foundation.
- Add phosphorus power: Mix in 1 cup of bone meal. This will encourage tons of blossoms.
- Incorporate potassium: Add 1/2 cup of kelp meal or wood ash to help the plant develop strong fruit and stay vigorous.
Use this blend as a "side-dressing" by scratching it into the soil around the base of your plants right when you see the first flowers starting to form. By understanding both the ready-to-use convenience of commercial products and the custom power of your own blends, you can confidently choose the path that will lead you to your best harvest yet.
How to Apply Fertilizer for the Best Results
Having the perfect organic fertilizer is only half the job. Knowing exactly when and how to use it is what separates a decent garden from a truly bountiful one. It's a bit like being a great chef—you might have the best ingredients, but your timing and technique are what create a masterpiece.
The real key is to match your feeding schedule to what your plants actually need at each stage of their life. You're aiming to give them the right support at the right time, from building a strong foundation early on to fueling the final push for flowers and fruit.
Before You Even Plant
Honestly, the most crucial feeding your garden will ever receive happens before you even think about putting a seed in the ground. This is your chance to build a rich, nutrient-dense foundation for the entire season. For this, granular, slow-release fertilizers are your best friend.
As you're turning over your garden beds in the spring, that's the perfect moment to mix in these nutrients. Just sprinkle the fertilizer evenly over the soil, following the instructions on the bag, and then gently work it into the top 4-6 inches. If you want a full walkthrough, our detailed guide on preparing garden soil covers this process step-by-step.
Mid-Season Boosts with Side-Dressing
Around the middle of the growing season, you’ll notice that your hungriest plants—think tomatoes, corn, and squash—are starting to look for another meal. This is the perfect time for a technique called side-dressing. Think of it as a well-timed energy snack for your garden’s star performers.
Here’s how to do it:
- Gently pull back any mulch from around the base of the plant.
- Scratch a shallow trench a few inches away from the main stem.
- Sprinkle a bit of granular organic fertilizer into the trench you just made.
- Cover the fertilizer back up with soil and give it a good watering to get it working.
Side-dressing is incredibly effective because it puts nutrients right where they’re needed most—the active root zone—without disturbing the plant. It's a much more targeted and efficient approach than just scattering fertilizer everywhere once your plants are established.
A Quick Pick-Me-Up with Foliar Feeding
Every now and then, a plant might look like it needs help fast, especially if it’s showing signs of a nutrient deficiency. This is where liquid fertilizers, like a fish emulsion or kelp meal tea, truly shine. The technique is called foliar feeding, and it’s as simple as spraying the liquid fertilizer directly onto the plant’s leaves.
Plants can absorb small amounts of nutrients through their foliage, making it the quickest delivery method you have. It’s fantastic for a quick fix, but think of it as a supplement, not a long-term substitute for healthy, well-fed soil.
The drive for smarter, more efficient ways to fertilize isn't just a backyard trend. The organic fertilizer market in Asia Pacific alone was valued at USD 5.18 billion in 2024 and is expanding quickly. New methods are helping everyone from home gardeners to large-scale farmers use fertilizer more effectively, which means less waste and bigger harvests. You can read more about these global market trends to see how organic practices are evolving worldwide.
Your Top Questions About Organic Vegetable Fertilizers, Answered
Once you start digging into organic gardening, a lot of questions pop up. It’s a whole different mindset from conventional gardening, so it's completely normal to feel a bit unsure at first. Think of this as your go-to FAQ, where we'll tackle the most common questions and myths I hear from fellow gardeners about organic fertilizers.
My goal here is to give you clear, no-nonsense answers that build your confidence. By the time we're done, you'll feel ready to make the right calls for your garden.
Can I Actually Over-Fertilize With Organic Stuff?
Yes, you definitely can! It's much harder to do than with synthetic chemicals, but it’s not impossible. Organic fertilizers are far more forgiving, but piling on too much of a good thing can still cause trouble, especially with high-nitrogen sources like pure blood meal or fresh, uncomposted manure.
The classic sign of overdoing it with nitrogen is a plant that explodes with lush, deep green leaves but gives you hardly any flowers or fruit. You might end up with a tomato plant that looks like a prize-winning bush but only produces a handful of tomatoes. In more severe cases, a super-concentrated dose can even cause "nutrient burn," leaving you with brown, crispy leaf edges and stressed-out plants.
The golden rule of organic gardening is to feed the soil, not just the plant. Piling on fertilizer disrupts the delicate ecosystem of microbes in your soil. A slow, steady approach will always win out for the long-term health of your garden.
How Long Does It Take for Organic Fertilizer to Start Working?
That’s a great question, and the answer really comes down to what kind of fertilizer you're using. I like to think of it as the difference between grabbing fast food and cooking a slow-cooked meal.
- Liquid Fertilizers (The Fast Food): Products like fish emulsion are basically on-demand nutrients for your plants. Since they're already dissolved in water, the roots can slurp them up immediately. You’ll often see a visible perk-up, like greener leaves, in just a few days. This makes them perfect for giving seedlings a gentle boost or helping a struggling plant get back on its feet.
- Granular Fertilizers (The Slow-Cooked Meal): These are the true workhorses of an organic garden. Ingredients like bone meal, kelp meal, and compost need time. The microorganisms in your soil have to break them down first to unlock the nutrients for your plants. It's a natural, biological process that can take weeks or even months.
This slow-release feature is one of the biggest benefits of going organic. It provides a steady, gentle stream of food for your plants all season long, avoiding the harsh boom-and-bust cycle you get with chemical feeds. Plus, it builds incredible soil structure over time.
Is Compost All My Garden Really Needs?
Compost is the undisputed champion of the organic garden. We call it "black gold" for a reason! It provides a fantastic, balanced foundation of nutrients, beneficial microbes, and rich organic matter that works wonders for soil structure. For many plants that aren't too demanding, a healthy dose of compost is all they'll ever need.
But think of compost as a healthy, well-rounded daily diet. For your "heavy feeders"—the vegetables with huge appetites—you'll see a massive improvement by giving them a little extra something.
These hungry crops include vegetables like:
- Tomatoes
- Corn
- Broccoli
- Squash
- Cabbage
For these guys, supplementing your compost with specific amendments makes all the difference. Tossing in some bone meal for extra phosphorus to encourage more flowers, or some kelp meal for potassium to improve overall plant health, will address their specific cravings. This strategy is what takes a harvest from just "good" to truly great.
What's the Real Difference Between "Organic" and "Natural" Fertilizer?
This is a big one. People use these terms interchangeably all the time, but they can mean very different things. It’s really a matter of marketing versus certification, and knowing the difference helps you understand what you're actually putting on your soil.
A "natural" fertilizer just means its ingredients come from plants, animals, or mined minerals with minimal processing. That sounds good on the surface, but the term isn't regulated. A product can be labeled "natural" and still contain things you might not want in a truly organic garden.
An "organic" fertilizer, especially one with a certification like the OMRI Listed® logo, is a guarantee. That seal means an independent organization has checked every single ingredient and the entire manufacturing process. They've confirmed it meets the strict standards of the National Organic Program, ensuring it's free of synthetic chemicals, GMOs, and other prohibited stuff. For true peace of mind, always look for that OMRI seal when you're buying a commercial organic vegetable fertilizer.
Ready to start building healthier soil and growing more nutritious vegetables? At Homegrown Garden, we offer a curated selection of heirloom seeds and organic gardening supplies to help you succeed. Explore our gardening kits and guides to find everything you need for your best harvest yet.



